Abstract:
Objective To explore the efficacy and safety of single-port plus one laparoscopic radical resection for colorectal cancer in patients with colorectal cancer.
Methods A total of 78 patients with colorectal cancer admitted from January 2021 to December 2023 were selected as the research objects. They were divided into the observation group (n=39, undergoing single-port plus one laparoscopic radical resection for colorectal cancer) and the control group (n=39, undergoing conventional 5-port laparoscopic radical resection for colorectal cancer) using the random number table method. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 25.0 software. Enumeration data were expressed as percentages, and comparisons were made using the χ2 test. Measurement data conforming to normal distribution were expressed as (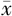 ±s); independent sample t test and paired sample t test were used for inter-group and intra-group comparisons, respectively. Rank sum test was used for ranked data. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
±s); independent sample t test and paired sample t test were used for inter-group and intra-group comparisons, respectively. Rank sum test was used for ranked data. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The incision length, time to first flatus, time to ambulation, gastrointestinal function recovery time, and hospital stay in the observation group were significantly shorter than those in the control group (P<0.05). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of maximum tumor diameter, distance of proximal and distal tumor resection margins, or number of lymph nodes dissected (P>0.05). The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores on the 1st and 3rd days after surgery in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), norepinephrine (NE), cortisol (COR), and adrenaline (AD) in the observation group were all lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The incidence of complications such as incision infection, subcutaneous emphysema, anastomotic bleeding, urinary retention, and intestinal obstruction in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusion The implementation of SILS+1 laparoscopic radical resection for colorectal cancer in patients with colorectal cancer can effectively shorten the hospital stay, reduce postoperative pain, inflammatory response, and stress response. It achieves a definite tumor radical effect, reduces the incidence of complications, promotes postoperative recovery, and has high safety.
Key words:
Colorectal Neoplasms,
Laparoscopes,
Single Port+1 Laparoscopic Radical Resection of Colorectal Cancer,
Safety,
Inflammatory Response
Zhengyuan Yan, Heng Zhang, Nengqi Cao, Xingchao Fang, Damin Chen. Clinical observation on the efficacy and safety of single-port plus one laparoscopic radical resection for colorectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2025, 19(06): 615-618.