Abstract:
Objective To observe the impact of prophylactic ileostomy via median incision on postoperative recovery and complication incidence in patients undergoing laparoscopic radical resection of rectal cancer.
Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on the clinical data of patients who underwent laparoscopic radical resection of rectal cancer from June 2022 to June 2024. Patients receiving prophylactic ileostomy via median incision were enrolled in the observation group, and those receiving prophylactic ileostomy via traditional incision were included in the control group. Propensity score matching was used for 1:1 matching of the two groups, with 54 pairs of patients showing no significant baseline differences included in the study. Data were analyzed using SPSS24.0 software. Measurement data were expressed as (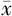 ±s), and independent sample t tests and paired sample t tests were performed; enumeration data were expressed as percentages, and Fisher’s exact probability test or χ2 test was applied; Rank Sum test was used for ordinal data comparison. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
±s), and independent sample t tests and paired sample t tests were performed; enumeration data were expressed as percentages, and Fisher’s exact probability test or χ2 test was applied; Rank Sum test was used for ordinal data comparison. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The interval between stoma reversal surgeries in the observation group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (P<0.05), but there were no significant differences in reversal surgery time or intraoperative blood loss between the two groups (P>0.05). At 72 hours postoperatively, the visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in both groups were lower than those at 24 hours postoperatively, and the observation group had significantly lower scores than the control group (P<0.05). At 24 hours postoperatively, serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased in both groups, but the observation group had lower serum CRP, PCT, and TNF-α levels than the control group (P<0.05). The total incidence of complications in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusion Prophylactic ileostomy via median incision is more conducive to postoperative recovery, alleviates postoperative pain, and reduces the incidence of postoperative complications compared with ileostomy via traditional incision, with no significant impact on stoma reversal surgery time or intraoperative blood loss. Clinically, the appropriate stoma method should be selected based on patients’ needs and actual conditions.
Key words:
Rectal Neoplasms,
Laparoscopes,
Median Incision,
Prophylactic Ileostomy
Yanling Xiao, Shenglan Du, Chunmei Yang, Zhengwen Xu, Mei Wang. Application of median incision in prophylactic ileostomy for laparoscopic radical resection of rectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2025, 19(05): 539-542.