Abstract:
Objective To compare the clinical effects of laparoscopic-assisted radical distal gastrectomy via different approaches in the treatment of advanced distal gastric cancer.
Methods The clinical data of 92 patients with advanced distal gastric cancer who underwent laparoscopic-assisted radical distal gastrectomy from April 2020 to April 2023 were retrospectively collected. According to different surgical approaches, they were divided into the right-sided group (n=47) and the left-sided group (n=45). SPSS25.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. Measurement data such as clinical data were described by (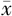 ±s), and t test was performed; enumeration data such as gender were described by [cases (%)], and chi-square test was performed. The Kaplan-Meier curve was used to analyze the survival of patients 12 months after operation.
±s), and t test was performed; enumeration data such as gender were described by [cases (%)], and chi-square test was performed. The Kaplan-Meier curve was used to analyze the survival of patients 12 months after operation.
Results the operation time of the right-sided group was shorter than that of the left-sided group, and the number of lymph nodes dissected was more than that of the left-sided group (P<0.05); there was no significant difference in postoperative exhaust, out-of-bed activity, and hospital stay between the two groups (P>0.05). The tests of group, time point, and interaction effect between group and time point of C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the two groups were statistically significant (P<0.05); CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 in the right-sided group were lower than those in the left-sided group at 3 days and 7 days after operation (P<0.05). The levels of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), carbohydrate antigen 199 (CA199), and CA125 in the two groups were lower than those before operation at 1 week after operation, but there was no significant difference between the groups (P>0.05). There was no significant difference in the survival of the two groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion The left-sided approach and the right-sided approach can achieve comparable survival at 12 months after operation, but compared with the left-sided approach, the right-sided approach can increase the number of lymph nodes dissected in laparoscopic-assisted radical distal resection, shorten the operation time, and reduce the degree of perioperative inflammatory response.
Key words:
Advanced Distal Gastric Cancer,
Radical Distal Gastrectomy,
Laparoscopes,
Lymph Nody Excision
Yuhao Jia, Kunyu Lv, Zhiqiang Liu, Baozhong Li. Clinical comparison of laparoscopic-assisted radical distal gastrectomy via different approaches for advanced distal gastric cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2025, 19(05): 513-516.