Abstract:
Objective To investigate the risk factors of splenic hilar lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer.
Methods The clinical data of 150 patients with upper gastric cancer from January 2020 to January 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Lymph node metastases or micrometastases were detected by immunohistochemical methods. SPSS 20.0 was used for data analysis. Measurement data were expressed as (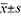 ) and independent sample t test was used. The counting data were expressed by frequency and χ2 test was used. Multivariate Logistic regression was used to analyze the independent factors affecting hilar lymph node metastasis, micrometastasis and total metastasis. The influence of gender on the relationship between independent factors and hilar lymph node metastasis was analyzed using the layered interaction test in Empower Stats software. The structural equation model of hilar lymph node metastasis was constructed based on the important factors of screening and analyzed and tested. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
) and independent sample t test was used. The counting data were expressed by frequency and χ2 test was used. Multivariate Logistic regression was used to analyze the independent factors affecting hilar lymph node metastasis, micrometastasis and total metastasis. The influence of gender on the relationship between independent factors and hilar lymph node metastasis was analyzed using the layered interaction test in Empower Stats software. The structural equation model of hilar lymph node metastasis was constructed based on the important factors of screening and analyzed and tested. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results Among the 150 patients, 33 patients had hilar lymph node metastasis, with a metastasis rate of 22.0% (33/150). Among the 117 patients with negative routine pathology, 38 patients had hilar lymph node micrometastasis, with a metastasis rate of 32.5% (38/117). The overall transfer rate was 47.3% (71/150). Transverse location of tumor, Bormann classification, No.4sa lymph node metastasis, TNM stage, depth of invasion, No.2 lymph node metastasis and No.4sb lymph node metastasis were independent factors of total hilar lymph node metastasis (P<0.05). Based on the above risk factors, the structural equation model affecting the overall lymph node metastasis was further constructed, which could effectively reflect the relationship between the study variables and the overall lymph node metastasis. The verification model has good differentiation and accuracy.
Conclusion Major curved side, No.4sa lymph node metastasis, Bormann classification Ⅲ-Ⅳ, No.4sb lymph node metastasis, submucosal infiltration, Ⅲ-Ⅳ stage, No.2 lymph node metastasis were independent factors of total hilar lymph node metastasis. In this study, the structural equation model established to affect the overall lymph node metastasis has a good overall fit, and the verified model has a good degree of differentiation and accuracy.
Key words:
Stomach Neoplasms,
Lymphatic Metastasis,
Risk Factors,
Structural Equation Model
Bin He, Jinfeng Ma. Risk factors for splenic hilar lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(06): 694-699.