Abstract:
Objective To understand the clinical efficacy and adverse reactions of polymyxin-based combination therapy for carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB), Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA), and to provide reference for rational clinical application of polymyxins.
Methods The clinical data of 42 patients treated with polymyxins from January 2019 to August 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. SPSS 24.0 software was used for data analysis. Measurement data were represented by (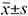 ) and independent sample t test was adopted. The statistical data were expressed as [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
) and independent sample t test was adopted. The statistical data were expressed as [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results 42 cases treated with polymyxin combined with anti-infection, 28 cases were effective and 14 cases were ineffective, the effective rate was 66.7%. The effective rate of polymyxin B (72.4%) was higher than that of polymyxin E (53.8%), and there was statistical difference between the two groups (P<0.05). The duration of antibiotic use before polymyxin application affected the curative effect of the patients. When the duration of antibiotic use was changed to polymyxin within 14 days, the effective rate was 73.3% (30/42), which was better than the effective rate of 50% (21/42) after 2 weeks (P<0.05). The clearance rate of CRPA was higher, while the clearance rate of CRKP and CRAB was lower. CRP and PCT were significantly decreased (P<0.05). Nephrotoxicity was the main adverse reaction after polymyxin treatment, the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) was 16.7%, and the incidence of polymyxin E nephrotoxicity was 38.5%, which was higher than that of polymyxin B 6.9%.
Conclusion Polymyxin-based combination therapy is effective in the treatment of CRAB, CRKP and CRPA bacterial infections, and the efficacy of polymyxin-B is better than polymyxin-E. The main adverse reaction of polymyxin was nephrotoxicity, and the incidence of nephrotoxicity of polymyxin E was higher than that of polymyxin B. The monitoring of renal function should be strengthened during use, and the simultaneous use of other drugs with renal function injury should be avoided.
Key words:
Polymyxin B,
Bacterial Infections,
Treatment Outcome,
Clinical Effect,
Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Yuefang Xu, Wang Liu, Miaotian Zeng, Yushu Guo. Clinical efficacy of polymyxin B and polymyxin E in the treatment of surgical multi-drug resistant infections Security analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(06): 700-703.