Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the value of plasma BRAF gene detection for pyloric lymph node dissection during laparoscopic D3 radical resection of right colon cancer.
Methods A total of 98 patients undergoing laparoscopic D3 radical resection of right colon cancer from March 2019 to February 2021 were prospectively selected as the study subjects. SPSS 25.0 software was used to process the data. Statistical data were presented as [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. The normal data were represented by (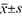 ), and the inter-group comparison line independent sample t test; Consistency was tested by Kappa coefficient. ROC curve was drawn to test the efficacy of BRAD gene mutation in evaluating the metastasis and recurrence of right subpyloric lymph node of colon cancer. P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
), and the inter-group comparison line independent sample t test; Consistency was tested by Kappa coefficient. ROC curve was drawn to test the efficacy of BRAD gene mutation in evaluating the metastasis and recurrence of right subpyloric lymph node of colon cancer. P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
Results All 98 patients with right hemicolonic carcinoma successfully completed laparoscopic D3 radical resection. 45 patients with positive plasma BRAF gene received subpyloric lymph node dissection, while 53 patients with invisible plasma BRAF gene did not receive subpyloric lymph node dissection. The proportion of TNM stage Ⅲ, hepatocellular carcinoma, proximal transverse colon cancer and BRAF gene mutation in patients with subpyloric lymph node dissection was higher than that of patients without dissection, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). BRAF gene mutation in the evaluation of right hemicolonic carcinoma subpyloric lymph node metastasis and pathological diagnosis showed a strong consistency (Kappa=0.604). ROC data showed an AUC of 0.788 for BRAF mutations evaluating subpyloric lymph node metastasis in right colon cancer. The coincidence rate between postoperative recurrence of right colon cancer assessed by BRAF mutation and follow-up was 90.0%. ROC data showed that the AUC of BRAF gene mutations evaluating postoperative recurrence and metastasis of right colon cancer was 0.628.
Conclusion BRAF gene mutation in patients with right hemicolonic carcinoma increases the risk of postoperative recurrence and metastasis by increasing the risk of subpyloric lymph node metastasis. Subpyloric lymph node dissection should be considered in patients with plasma BRAF gene mutation.
Key words:
Colonic Neoplasms,
Laparoscopes,
Lymph Node Excision,
BRAF Gene,
Recurrence
Zhixiang Ding, Peng Yu, Shaobin Duan. The value of plasma BRAF gene detection for pyloric lymph node dissection during laparoscopic D3 radical resection of right colon cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(05): 570-573.