Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) monitoring in unilateral thyroidectomy and central lymph node dissection without inflatable axillary approach.
Methods Retrospective analysis was performed on the clinical data of 94 patients who underwent unilateral thyroidectomy plus central lymph node dissection without aeration axillary approach from June 2020 to June 2022. The patients were divided into IONM group (n=45 cases) according to whether intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM) was used in combination with intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM). Intraoperatively IONM was used to protect recurrent laryngeal nerve (n=49 cases, routine identification of recurrent laryngeal nerve protection) and conventional group. SPSS 22.0 software was used for data statistics and analysis. Measurement data such as perioperative indexes and vocal indexes were expressed as (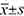 ). Independent sample t test was used for inter-group comparison. Statistical data such as postoperative complications were presented as [example (%)], and χ2 test was used for comparison between groups. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
). Independent sample t test was used for inter-group comparison. Statistical data such as postoperative complications were presented as [example (%)], and χ2 test was used for comparison between groups. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The operative time, RLN exposure time and central lymph node dissection time in IONM group were significantly shorter than those in conventional group, and the intraoperative blood loss and postoperative drainage volume were significantly lower than those in conventional group, with statistical significance (P<0.05). Fundamental frequency perturbation, whole amplitude perturbation and standardized noise energy of two groups were significantly decreased, harmonic noise ratio was significantly increased, and all indexes in IONM group were better than those in conventional group one month after surgery (P<0.05). The total complication rate in IONM group was significantly lower than that in traditional group (8.9% vs.26.5%, P<0.05).
Conclusion The combined application of IONM in the operation of unilateral thyroidectomy and central lymph node dissection without aeration armpit approach can rapidly and accurately locate RLN, effectively reduce the operation time and central lymph node dissection time, and is more beneficial to the protection of RLN, reduce the degree of RLN injury and the incidence of complications, and improve the safety of surgery.
Key words:
Thyroid Neoplasms,
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve,
Central Lymph Nodes,
Lymph Node Excision,
Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring,
Axillary Approach Without Inflation
Yifei Gao, Genxiang Liu, Changhua Sun, Guangjun Zhou. Application of recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in unilateral thyroidectomy and central lymph node dissection without inflatable axillary approach[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(05): 483-486.