Abstract:
Objective To explore the difference of the application effect of two different surgical approaches in the open radical operation of patients with papillary thyroid cancer.
Methods The clinical data of 98 patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma admitted from January 2019 to January 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were grouped according to the surgical method, and patients receiving medial paratRAC approach to thyroid gland were included in the observation group (n=48 cases), and patients receiving traditional lateral approach to thyroid gland were included in the control group (n=50 cases). Statistical software SPSS 26.0 was used to process the data. Statistical data such as prognosis were presented as [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. Intraoperative and postoperative measurement data were expressed as (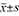 ), and independent sample t test was used between the two groups. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
), and independent sample t test was used between the two groups. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The operative time, intraoperative blood loss, postoperative extubation time and postoperative hospital stay in observation group were lower than those in control group, and the neck drainage volume in observation group was higher than that in control group (P<0.05). 30 days after surgery, PTH and Ca2+ levels in both groups decreased compared with those before surgery, and PTH and Ca2+ levels in observation group were higher than those in control group (P<0.05). The incidence of hypocalcemia, temporary hypoparathyroidism, temporary recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in observation group were lower than those in control group (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in 1-year survival rate, recurrence rate and distant metastasis between the two groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion Open radical surgery with medial paratransheal approach to thyroid gland is more convenient and can protect recurrent laryngeal nerve and parathyroid function in patients with papillary thyroid cancer with less adverse effects.
Key words:
Thyroid Neoplasms,
Carcinoma, Papillary,
Thyroidectomy,
Medial Paratracheal Approach,
Prognosis
Wen Gu, Shouxin Ling, Haili Tang, Xuemei Gan. Comparison of two different surgical approaches for open radical surgery in patients with papillary thyroid cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(06): 687-690.