Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of pancreatic duct stenting in the treatment of acute biliary pancreatitis (ABP).
Methods A total of 104 ABP patients from January 2021 to January 2023 were prospectively selected and divided into two groups by random number table method, with 52 patients in each group. Patients in the control group received laparoscopic surgery, and patients in the observation group received laparoscopic surgery plus pancreatic duct stent implantation. SPSS 27.0 software was used for statistical analysis. Measurement data such as hematuric amylase and lipase indexes, stress response indexes, liver function changes, and inflammatory factor indexes were expressed as (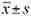 ), and independent sample t test was used. Complications were represented by [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
), and independent sample t test was used. Complications were represented by [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The duration of abdominal pain, fever, leukocyte increase and hospitalization in observation group were shorter than those in control group (all P<0.05).After operation, the levels of serum amylase (S-AMY), urine amylase (U-AMY) and lipase, direct bilirubin (DBIL), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), interleukin-6 (IL-6), hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and tumor necrosis fact-α (TNF-α) in observation group were lower than those in control group, the difference were statistically significant (P<0.05). The complication rate of observation group (3.8%) was lower than that of control group (19.2%), P<0.05.
Conclusion Pancreatic duct stenting for ABP can shorten the duration of symptoms and hospital stay, reduce the levels of amylase and lipase in blood and urine, improve liver function, reduce inflammation and reduce complications.
Key words:
Pancreatitis,
Pancreatic Duct Stent Implantation,
Cholecystectomy, Laparoscopic,
Acute Biliary Pancreatitis,
Postoperative Complications
Chanjuan Kang, Haitao Zhang, Jingjie Zhai. Effect of pancreatic duct stent implantation in the treatment of acute biliary pancreatitis and its influence on liver function and levels of inflammatory factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(06): 667-670.