Abstract:
Objective To analyze the impact of preoperative nutritional support combined with early postoperative enteral nutrition (EN) on the prognosis of patients undergoing rectal cancer surgery.
Methods Rectal cancer patients who underwent surgery from May 2022 to May 2024 were enrolled and divided into three groups using a random number table: Group A (preoperative nutritional support + early postoperative EN), Group B (preoperative nutritional support + early postoperative oral carbohydrate and liquid diet transition), and Group C (routine preoperative preparation + liquid diet transition after postoperative exhaust), with 30 patients in each group. Data were analyzed using SPSS 25.0. Measurement data such as postoperative recovery and nutritional status were described as (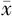 ±s), and analyzed by One-Way ANOVA with LSD-t test for pairwise comparisons between groups; enumeration data such as gender were described as [cases (%)] and analyzed by χ2 test. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
±s), and analyzed by One-Way ANOVA with LSD-t test for pairwise comparisons between groups; enumeration data such as gender were described as [cases (%)] and analyzed by χ2 test. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The (nutritional intake compliance rate) of Groups A, B, and C was 80.0%, 83.3%, and 76.7%, respectively, with no significant difference among groups (P>0.05). The postoperative hospital stay, first exhaust time, and first defecation time in Group A were shorter than those in Groups B and C, and Group B was shorter than Group C (P<0.05). At 7 days postoperatively, serum total protein (TP), albumin (ALB), and prealbumin (PALB) decreased in all three groups, but Group A had higher levels than Groups B and C, and Group B had higher levels than Group C (P<0.05). At 7 days postoperatively, C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increased in all three groups, but Group A had lower levels than Groups B and C, and Group B had lower levels than Group C (P<0.05).
Conclusion Preoperative nutritional support combined with early postoperative EN for rectal cancer surgery patients can improve nutritional status, reduce the degree of inflammatory stress, and facilitate early rehabilitation.
Key words:
Rectal Tumors,
Nutritional Support,
Prognosis,
Treatment Outcome
Qiyin Xu, Shangzhi Han. Impact of preoperative combined with postoperative nutritional support on rehabilitation of patients with rectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2025, 19(05): 543-546.