Abstract:
Objective To study 3D laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) combined with obesity and observe its clinical efficacy, and analyze the factors influencing LSG in the treatment of T2DM.
Methods Clinical data of 65 obese patients with T2DM treated with LSG from January 2019 to January 2022 were reviewed and analyzed. Follow-up was performed at months 1, 3, 6, and 12 within 1 year after surgery. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0, and the measurement data were expressed as (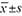 ) deviation with independent samples t test. Count data were analyzed using the χ2 test, and logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the multiple factors affecting clinical outcomes. Differences were considered statistically significant at P<0.05.
) deviation with independent samples t test. Count data were analyzed using the χ2 test, and logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the multiple factors affecting clinical outcomes. Differences were considered statistically significant at P<0.05.
Results All patients completed 1-year postoperative follow-up, and no patients dropped out. BMI, fasting glucose (FPG), fasting C-peptide, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), total cholesterol (CHOL), triglycerides (TG), and fasting insulin levels (FINS) were all in remission at 1 year postoperatively. Multivariate analysis showed that the duration of T2DM disease, C-peptide, and FINS were factors influencing the efficacy of T2DM after LSG.
Conclusion LSG has a significant therapeutic effect on T2DM patients while reducing body weight, but its long-term efficacy needs further validation.
Key words:
Sleeve Gastrectomy,
Bariatric Surgery,
Laparoscopy,
Obesity,
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Shuai Zhao, Wei Wang, Ruiqi Li, Jiajie Zhou, Daorong Wang. Clinical efficacy and influencing factors of 3D laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for the treatment of obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(02): 146-149.