Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical effect of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) in the treatment of obesity complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and fatty pancreas.
Methods Clinical data of 63 obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and adipopancreatitis treated with LSG from January 2021 to Qctober 2022 were retrospectively analyzed, and the weight loss effect, metabolic indexes and pancreatic function indexes before and after surgery were analyzed, and the remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus, adipopancreatitis and other complications were statistically analyzed 12 months after surgery. SPSS 25.0 was used to analyze the data. The measurement data of physical indexes, blood glucose and lipid metabolism indexes were expressed as (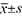 ), and paired sample t-test was used. Statistical data such as comorbidities are presented as [cases (%)]. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
), and paired sample t-test was used. Statistical data such as comorbidities are presented as [cases (%)]. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results Compared with pre-operation, At 6 and 12 months after surgery, the patient's body weight, body mass index (BMI), percentage of excess weight loss (EWL%), waist circumference, hip circumference, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and other physical indexes, fasting blood glucose (FPG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting insulin (FINS), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), and low density lipoprotein (LDL) The blood glucose and lipid metabolism indexes such as LDL-C and high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) showed a decreasing trend, and the levels of these indexes were significantly lower at 12 months after surgery than at 6 months after surgery (P<0.05). Compared with the preoperative results, the insulin resistance index (Homa-IR) and islet beta cell function (Homa-β) level of the patients were significantly decreased at 6 and 12 months after surgery, and the Homa-IR level at 12 months after surgery was significantly lower than that at 6 months after surgery, and the Homa-β level at 12 months after surgery was significantly higher than that at 6 months after surgery (P<0.05). By 12 months after surgery, the remission rate of type 2 diabetes was 71.4%, and the remission rate of comorbidized fatty pancreatitis, hypertension, and hyperlipidemic was 82.5%, 77.8%, and 81.8%, respectively.
Conclusion LSG is safe and effective in the treatment of obesity combined with type 2 diabetes and adipose pancreas, and can achieve significant weight loss effect, while improving the metabolism of blood sugar, blood lipids and pancreatic function, and most patients can achieve diabetes remission and adipose pancreas remission after surgery.
Key words:
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy,
Obesity,
Type 2 Diabetes,
Fatty pancreas
Meng Li, La Jiang, Lei Dong, Qing Wu, Ben Li Jia. Clinical study of laparoscopic gastric sleeve resection in the treatment of obesity complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and fatty pancreas[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(05): 554-557.