Abstract:
Objective To compare and analyze the near and long term effects of laparoscopic hepatectomy (LH) for early ICC (intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma) in different lymph node dissection (LND) ranges.
Methods Seventy-six patients with early ICC who received LH in our hospital from January 2020 to December 2022 were selected as the study objects, and the patients were divided into standard LND group and local LND group by random number table method, with 38 cases in each group. LH was administered to both groups. Standard LND group: standardized LND was administered, and local LND group: local LND was administered. Data analysis was completed by SPSS 25.0, and the difference was statistically significant as P<0.05. Measurement data such as surgery-related indicators were expressed as (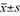 ), and independent t test was used; The statistical data of postoperative complications were expressed as [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. Kaplan-Meier method was used to draw the survival curve and calculate the survival rate, and Log-Rank test was used for survival analysis.
), and independent t test was used; The statistical data of postoperative complications were expressed as [cases (%)] and χ2 test was used. Kaplan-Meier method was used to draw the survival curve and calculate the survival rate, and Log-Rank test was used for survival analysis.
Results The operation duration, blood loss and number of LND in local LND group were significantly reduced compared with standard LND group (P<0.05), but there were no significant differences in the number of positive LND, first postoperative exhaust time, postoperative drainage tube indwelling time and postoperative hospital stay between the two groups (P>0.05). There was no significant difference in the total incidence of postoperative complications between local LND group (10.5%) and standard LND group (18.4%) (P>0.05). During follow-up, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that cumulative disease-free survival (78.9% vs. 73.7%) and cumulative overall survival (84.2% vs. 78.9%) of patients in the standard LND group and the local LND group were compared. There was no significant difference (Log-Rankχ2=0.158, 0.039, P=0.691, 0.843).
Conclusion Compared with standardized LND, although local LND in LH for early ICC patients can narrow the cleaning range and reduce the number of LND, there is no significant difference in the number of positive LND, and it can effectively shorten the operation time and reduce intraoperative injuries, and achieve long-term efficacy comparable to that of standardized LND.
Key words:
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma,
Laparoscopic Hepatectomy,
Lymph Node Dissection
Jinhua Zhang, Suo Zhao. A comparative study of the near and long term effects of early ICC laparoscopic hepatectomy in different lymph node dissection ranges[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(05): 578-581.