Abstract:
Objective To compare and analyze the clinical efficacy of ERCP sequential surgery versus one-stage surgery in the treatment of hepatic cystic echinococcosis (CE) with biliary rupture.
Methods A total of 28 patients with hepatic CE complicated by biliary rupture, treated from January 2016 to August 2021, were selected. According to the different surgical methods, they were divided into the observation group (ERCP sequential surgery, n=13) and the control group (one-stage surgery, n=15). Inflammatory indicators, liver function, primary lesion management methods, surgical indicators, recurrence rate, and complications were compared between the two groups. Statistical software SPSS 25.0 was used for data analysis. Normality test was first performed on the measurement data: those conforming to normal distribution were expressed as (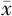 ±s), and independent samples t test was used for inter-group comparison; those not conforming to normal distribution were expressed as median (interquartile range) and analyzed by non-parametric rank-sum test. Chi-square test or exact probability method was used for inter-group comparison of count data. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
±s), and independent samples t test was used for inter-group comparison; those not conforming to normal distribution were expressed as median (interquartile range) and analyzed by non-parametric rank-sum test. Chi-square test or exact probability method was used for inter-group comparison of count data. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results After treatment, the inflammatory indicators and liver function indicators of both groups improved (P<0.05), but there was no statistically significant difference in these indicators between the two groups (P>0.05). The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, and postoperative extubation time in the observation group were shorter than those in the control group (P<0.05). The recurrence rate in the observation group (7.7%) was lower than that in the control group (20.0%), but the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of complications between the two groups (P>0.05), but the severity of complications in the observation group was milder.
Conclusion ERCP sequential surgery has significant clinical efficacy. It can effectively control biliary infection, relieve obstruction, and improve patients’ symptoms. It enables patients with severe conditions who cannot tolerate surgery to undergo treatment, effectively reduces surgical risks, and accelerates patient recovery, which is worthy of clinical promotion.
Key words:
Hepatic Cysticercosis,
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography,
Breakthrough Into The Biliary Tract
Aikbai Ainiwaer, Yilihaer Yierfan, Aji Tuerganaili. Clinical efficacy of ERCP sequential surgery versus one-stage surgery for hepatic cystic echinococcosis with biliary rupture[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2026, 20(01): 42-45.