Abstract:
Objective To investigate the efficacy monitoring and clinical significance of circulating tumor cell (CTC) capture system with CellCollector in breast cancer patients.
Methods Clinical data of 110 patients with breast cancer from January 2018 to December 2022 were retrospectively analyzed, and the patients were divided into CTC-negative group (n=34 cases) and CTC-positive group (n=76 cases) according to the results of CTC detection (threshold was 1). SPSS 23.0 software was used to analyze the data. Measurement data conforming to normal distribution were represented by (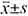 ), and independent sample t test was used for comparison between groups. The count data were presented as [cases (%)]. χ2 test or Fisher exact probability method were used for comparison between groups. Spearman method was used for correlation analysis. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
), and independent sample t test was used for comparison between groups. The count data were presented as [cases (%)]. χ2 test or Fisher exact probability method were used for comparison between groups. Spearman method was used for correlation analysis. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results In different clinical characteristics of breast cancer, the baseline positive CTC detection rate was significantly different in different molecular types (LuminalA, LuminalB, TNBC, HER-2 positive), HR (positive and negative groups), and Ki-67 (high, middle and low groups), with P values of 0.021, 0.043, 0.041, respectively. The results were statistically significant.
Conclusion The detection rate of CTC capture technology in CellCollector was high in breast cancer patients, and the detection rate was relate d to the molecular typing, HR typing and ki67 expression level of breast cancer, which provided a basis for CTC to identify the population with high recurrence risk and predict the prognosis.
Key words:
Breast Neoplasms,
Neoplastic Cells, Circulating,
CellCollector,
Molecular Typing
Lingyan Wang, Chunhui Gao, Xueyuan Feng, Xinmiao Cui, Huan Liu, Wenming Zhao, Jinku Zhang. Application of circulating tumor cells in neoadjuvant and postoperative adjuvant therapy for breast cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(06): 630-633.