Abstract:
Objective To explore the role of biological patch pelvic floor repair and direct suture in pelvic floor reconstruction in patients with low rectal cancer.
Methods Ninety patients with low rectal cancer treated in our hospital from June 2020 to June 2023 were selected as the study objects. All patients received laparoscopic perineal combined radical resection of rectal cancer (ARP), and were divided into biological mesh group (n=45) and direct suture group (n=45) according to intraoperative pelvic floor reconstruction methods. SPSS 22.0 was used for data analysis. Intraoperative conditions, maximum urine output, maximum urine flow rate and other measurement data were expressed as(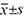 ), and independent sample t test was performed. The statistical data of postoperative complications were expressed by [cases (%)] and χ2 test was performed. P<0.05 indicates statistical difference.
), and independent sample t test was performed. The statistical data of postoperative complications were expressed by [cases (%)] and χ2 test was performed. P<0.05 indicates statistical difference.
Results The amount of intraoperative blood loss in the biological patch group was less than that in the direct suture group, and the time of extubation and perineal suture removal were significantly shorter than that in the direct suture group (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the operative time, hospital stay and postoperative mean maximum urine volume (P>0.05). The incidence of postoperative complications in biological mesh group was significantly lower than that in direct suture group, and the maximum urinary flow velocity was higher than that in direct suture group (P<0.05).
Conclusion Compared with direct suture pelvic floor repair, the application of biological patch after ARP is more effective in wound healing and complication prevention in patients with low rectal cancer.
Key words:
Rectal Neoplasms,
Pelvic Floor Repair,
Biological Patch,
Suture Technique
Chang Xue, Xiang Wang, Li Feng, Xin Jin, Zhiwei Wang. Application of biological patch pelvic floor repair and direct suture in pelvic floor reconstruction of patients with low rectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(03): 327-329.