Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between vitamin D level and prognosis of subacute thyroiditis (SAT).
Methods The clinical data of 170 SAT patients (SAT group) and 86 healthy subjects (control group) from March 2020 to March 2022 were retrospectively analyzed, and the 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels were compared and analyzed. SPSS 26.0 software was used for data analysis. Measurement data such as thyroid function test value and serum test value were expressed as (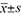 ), and independent sample t test was performed. The statistical data were represented by [example (%)] and χ2 analysis was used. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
), and independent sample t test was performed. The statistical data were represented by [example (%)] and χ2 analysis was used. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results The values of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), white blood cell count (WBC), free triiodothyronine (FT3) and free thyroxine T4 (FT4) in SAT group were higher than those in control group (P<0.001), and the values of 25(OH)D and TSH were lower than those in normal control group (P<0.001). The 25(OH)D level of 26 patients with relapse was (12.8±1.6) ng/ml, which was lower than that of non-relapse patients (14.2±1.9) ng/ml, and the difference was statistically significant (P=0.017). Among 170 SAT patients, 17 (10.0%) had permanent hypothyroidism after treatment, but there was no significant difference in 25(OH)D level between SAT and non-hypothyroidism patients (P=0.71).
Conclusion The level of vitamin D in patients with recurrent subacute thyroiditis after treatment is significantly lower than that in non-recurrent patients, indicating that targeted supplementation can reduce the recurrence rate.
Key words:
Thyroiditis Subacute,
Vitamin D,
Hypothyroidism
Qiuzi Zhang, Limei Hu, Yaru Chen, Li Zuo, Weidong Ren. Correlation between vitamin D level and prognosis of subacute thyroiditis[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(02): 217-219.