Abstract:
Objective To compare the effects of three different thyroidectomy methods on postoperative insulin resistance.
Methods Clinical data of 90 patients undergoing thyroidectomy from January 2019 to December 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. Based on different surgical methods, 30 patients undergoing unilateral adenoma resection were assigned to group A and 30 patients undergoing unilateral thyroidectomy were assigned to group B. Group C was assigned to 30 patients who underwent unilateral thyroidectomy + contralateral partial thyroidectomy. SPSS 26.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. Thyroid hormone and insulin resistance related indicators were expressed as (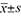 ), F test was used for inter-group comparison, and paired t test was used for intra-group comparison. P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
), F test was used for inter-group comparison, and paired t test was used for intra-group comparison. P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results The average weight of thyroidectomy in groups A, B and C was compared with group A < group B < group C (P<0.05). The levels of triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), serum free triiodothyronine (FT3) and serum free thyroxine (FT4) were lower than those before surgery, while the levels of thyrotropin (TSH) were higher than those before surgery. There were statistically significant differences in the above hormone levels at 7 days after operation compared with those before operation (P<0.05). The fasting blood glucose (FBG), 2 h postprandial blood glucose (2h PG), fasting insulin (FINS), 2 h postprandial insulin (2h INS), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) in groups A, B and C, especially in group C, were lower than those before thyroid surgery (P<0.05).
Conclusion The more thyroid tissue is removed, the more significant the reduction of thyroid hormone levels and the better the effect of improving insulin resistance. The basic theory of positive correlation between thyroid hormone levels and insulin resistance is supported by surgical evidence.
Key words:
Thyroid Nodule,
Triiodothyronine,
Thyroxine,
Thyrotropin,
Insulin,
Insulin Resistance
Benquan Wang, Fan Cui, Jun Qiu, Benhong Xiang. The effect of different thyroid surgery methods on improving insulin resistance[J]. Chinese Journal of Operative Procedures of General Surgery(Electronic Edition), 2024, 18(02): 208-211.